what test will show a muscle tear|grade 1 muscle strain symptoms : importers For a more serious muscle strain, your doctor may do an ultrasound to check for tears or fluid, or an MRI to check for blood clots or internal bleeding. Muscle Strain Treatment Autoclaves use water, pressure, and heat to create superheated steam that kills microorganisms and spores. Autoclaves at Princeton are used to decontaminate certain biological waste and sterilize media, instruments and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Class B autoclaves enable the sterilization of both wrapped and unwrapped instruments, no matter their type and complexity. The fractionated vacuum reduces the air in the sterilization chamber through repeated evacuation and .Our guide compares N, S, and B-type autoclave classes, ranking these sterilizers based on their differences and use in various settings. Autoclave classes: differences between N, S, and B-type sterilizers
For a more serious muscle strain, your doctor may do an ultrasound to check for tears or fluid, or an MRI to check for blood clots or internal bleeding. Muscle Strain Treatment For a more serious muscle strain, your doctor may do an ultrasound to check for tears or fluid, or an MRI to check for blood clots or internal bleeding. Muscle Strain Treatment During the physical exam, your doctor will check for swelling and points of tenderness. The location and intensity of your pain can help determine the extent and nature of the damage. In more severe injuries, where the muscle or tendon has been completely ruptured, your doctor may be able to see or feel a defect in the area of injury. To see any tears or other damage to your muscles and tendons and possibly ligaments, he or she will need to order an MRI scan, also called magnetic resonance imaging.
Your provider will classify your muscle strain by grade according to how severe it is: Grade 1 (mild). Grade 2 (moderate). Grade 3 (severe). What tests will be done to diagnose a muscle strain? If you have a more severe strain, your provider might use some imaging tests to diagnose your muscle strain: When Is Ultrasound Used vs. an MRI for Bone, Muscle and Joint Problems? Understand how these imaging tests differ. A muscle strain is an injury to a muscle or a tendon — the fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. Minor injuries may only overstretch a muscle or tendon, while more severe injuries may involve partial or complete tears in these tissues.The diagnosis is often achieved through a careful history and physical examination. Imaging may be recommended to evaluate the severity of the injury. Diagnostic ultrasound or MRI are excellent imaging modalities for evaluating soft tissue injuries such as muscle strains.
Computed tomography, or CT/CAT, is a non-invasive scan that produces X-ray images of the body, useful for diagnosing muscle sprains and strains.
A doctor can often diagnose a musculoskeletal disorder based on the history and the results of a physical examination. Laboratory tests, imaging tests, or other diagnostic procedures are sometimes necessary to help the doctor make or confirm a diagnosis. Muscle strain or a "pulled muscle" is an injury that causes stretching of the muscle fibers and can lead to a partial or complete tear of a muscle. These injuries typically occur: in muscles that cross two joints. during explosive action, such as sprinting. For a more serious muscle strain, your doctor may do an ultrasound to check for tears or fluid, or an MRI to check for blood clots or internal bleeding. Muscle Strain Treatment During the physical exam, your doctor will check for swelling and points of tenderness. The location and intensity of your pain can help determine the extent and nature of the damage. In more severe injuries, where the muscle or tendon has been completely ruptured, your doctor may be able to see or feel a defect in the area of injury.
abcam p24 elisa kit
To see any tears or other damage to your muscles and tendons and possibly ligaments, he or she will need to order an MRI scan, also called magnetic resonance imaging.
Your provider will classify your muscle strain by grade according to how severe it is: Grade 1 (mild). Grade 2 (moderate). Grade 3 (severe). What tests will be done to diagnose a muscle strain? If you have a more severe strain, your provider might use some imaging tests to diagnose your muscle strain: When Is Ultrasound Used vs. an MRI for Bone, Muscle and Joint Problems? Understand how these imaging tests differ. A muscle strain is an injury to a muscle or a tendon — the fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. Minor injuries may only overstretch a muscle or tendon, while more severe injuries may involve partial or complete tears in these tissues.The diagnosis is often achieved through a careful history and physical examination. Imaging may be recommended to evaluate the severity of the injury. Diagnostic ultrasound or MRI are excellent imaging modalities for evaluating soft tissue injuries such as muscle strains.
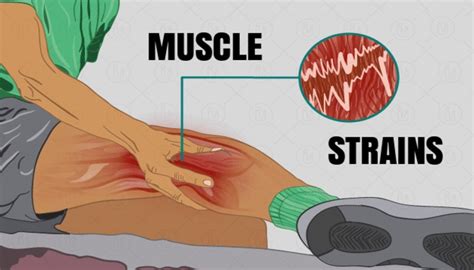
Computed tomography, or CT/CAT, is a non-invasive scan that produces X-ray images of the body, useful for diagnosing muscle sprains and strains.
A doctor can often diagnose a musculoskeletal disorder based on the history and the results of a physical examination. Laboratory tests, imaging tests, or other diagnostic procedures are sometimes necessary to help the doctor make or confirm a diagnosis.
abcam pge2 elisa kit
muscle tears away from bone
In food and beverage processing, autoclave sterilization tape is key for hygiene and safety — .
what test will show a muscle tear|grade 1 muscle strain symptoms